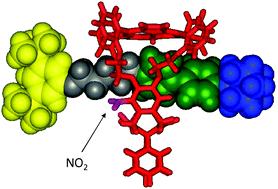
The development of synthetic catalysts that has parallel enzymatic efficiency in terms of rate and turnover is still a challenge in chemistry. The de novo design of a biochemical system in a molecular matrix is fascinating and challenging for future synthetic catalysis. We recently used a non-covalent interaction approach to create nano-sized artificial enzymes for the size, shape, stereo, and enantio-selective synthesis of small molecules and polymers.
Showing posts with label Chiral. Show all posts
Showing posts with label Chiral. Show all posts
Monday, December 24, 2018
Artificial polymerases
Saturday, March 15, 2008
Why are we made of only left-handed amino acids? A molecular concept of Life.
Most biomolecules are "chiral", that is to say, they exist in two left and right-handed mirror-image forms. However, biology only uses one hand, i.e., it is "homochiral". Life on Earth is made of left-handed amino acids, almost exclusively. One of the greatest puzzles in biophysics is the question of why life on Earth is based on left-handed (L) amino acids? Moreover, the synthesis of single enantiomers (ee ~100%) is one of the most critical industry demands.
Recently Prof. Pedro Cintas described that fractional sublimation of chiral organic compounds improves ee substantially.

The reported results provide a beneficial protocol for the resolution of racemates. Additionally, it suggests that improvement of optical activity by such a thermal process could be more efficient than or at least an alternative to spontaneous crystallization of suitable compounds.

He conclude that sublimation should be regarded as a reasonable mechanism for the formation of optically active crystals in the prebiotic world. Subsequent stochastic sorting of crystals of enantiopure compounds by natural agents might have generated highly enantiopure niches, which might be responsible for the prevalence of homochirality in nature.
Molecular evolution might lead to life, but it is not scientifically valid because life is a non-physical, non-chemical entity.
Saturday, November 10, 2007
The solvent makes the difference
The solvent surrounding the chiral molecule creates a chiral shell (Chiral Imprint). The chiroptical properties can originate mainly from the chiral solvent shell rather than from the chiral solute. For example, (S)-methyloxirane has a positive optical rotation in water but has a relatively strong negative value in benzene (P. Mukhopadhyay et al. Angew Chem Int Ed 2007, 46, 6450-6452).

Computational experiments by J Neugebauer (Angew Chem Int Ed 2007, 46, 7738-7740) shows the presence of the solute imprints a chiral structure on the inner solvation shell.
Saturday, September 8, 2007
Myers Asymmetric Alkylation
Psuedoephedrine is a chiral auxiliary used for the synthesis of enantiomerically enriched carboxylic acid, aldehyde, alcohol and ketones.


Both enantiomers of pseudoephedrine are inexpensive and can be N-acylated in high yields to generate its tertiary amides. In the presence of lithium chloride, the enolates of the corresponding pseudoephedrine amides undergo diastereoselective alkylations with a wide range of alkyl halides.
Advantages of using pseudoephedrine as chiral auxiliary,
• Enolate of pseudoephedrine amide undergoes efficient and high diastereoselective alkylation with a wide variety of alkyl halides,
• High enantiomerically enriched carboxylic acids, alcohols, aldehydes, and ketones, and
• Large scale/ Preocess application ( low cost of the auxiliary, the crystallinity of starting materials and products, no requirement of carcinogenic solvents.)
Ref: Myers, A.G. et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1997, 119, 6496.
Friday, September 7, 2007
Racemic Switch
A racemic switch or chiral switch is the redevelopment in the single-enantiomer form of a drug that was first approved as a racemates (racemic mixture). Sometimes, the pharmaceutical activity of a racemic mixture is present only in one enantiomer, and the other is inactive, or the other enantiomer has an undesired activity from the first.
 Omeprazole
OmeprazoleFor exmaple, Omeprazole is an Antiulcer drug (AstraZeneca) marketed in the U.S. as a racemic drug in 1995. It s a racemic mixture of R-omeprazole and S-omeprazole. Since its patent ran out in 2002 and the pharmacological activity lies in (S)-enantiomer, the company has patented now (S)-omeprazole named as esomeprazole.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)